THE GREAT SLOWDOWN: 10 REASONS WHY THE ECONOMY WILL STRUGGLE IN Q2
The new quarter is here, but unfortunately, we're still seeing the same bad trend as before. There are several problems we're facing, such as lost pricing power, tighter credit, not having enough money to spend, and more situations that are making things harder for people. It's also affecting the way businesses are performing.
We need to be careful because the situation is fragile and there are risks involved. We need to update our plans and be vigilant as we potentially go deeper into the woods of the bear market. It's crucial that we carefully watch out for what might happen next.
For a while now, there have been a lot of problems building up in this economy where we've seen a slowdown in growth and increase of inflation. Here are 10 indicators that suggest economic conditions will continue to decline in Q2.
1. Real Goods consumption has been in a downward trend since March 2021 [1]
When people stop buying things they need, like food, clothes, and electronics, it can cause big problems for the economy. This is because when people aren't buying goods, companies aren't making money, and they may have to lay off workers. When more people lose their jobs, they have less money to spend, which means they buy even fewer things. This creates a cycle where the economy slows down and things get worse for everyone.
One reason people might stop buying things is if prices are too high. When prices are high, people may decide they don't need to buy as much, or they might look for cheaper options. This can cause companies to lose money and may force them to cut jobs or raise prices even more. Another reason people might stop buying things is if they don't have enough money. When people are struggling financially, they may prioritize paying bills over buying new things, which can hurt the economy.
2. Real manufacturing orders have been going down since mid 2022 [2]
Real manufacturing orders are a measure of the amount of goods that companies are ordering from manufacturers. When real manufacturing orders are going down, it means that companies are not buying as many goods from manufacturers as they used to. This can be a sign that the economy is slowing down because if companies are not buying as many goods, it may be a sign that they are not selling as much to their customers either.
This decline in real manufacturing orders can also lead to a decrease in employment because if companies are not buying as many goods from manufacturers, then the manufacturers may need to lay off workers. This can lead to a ripple effect throughout the economy as those laid off workers may have less money to spend on other goods and services, which can further slow down the economy. Additionally, if there is a decrease in demand for goods, it can also lead to a decrease in production, which can impact the profitability of manufacturers and other related industries.
3. Capital Expenditures is going down since March of 2022 [3]
Capital expenditures (also known as CapEx) is the money that businesses spend on long-term investments such as building new factories, buying equipment, or developing new technology. When businesses are spending less on these types of investments, it often means that they are not confident about the future of the economy.
When capital expenditures are going down, it can have a ripple effect throughout the economy. For example, if a business is not investing in new equipment, it may mean that they are not expanding their production capacity. This could lead to a decrease in jobs, as there is less demand for labor. It could also mean that the business is not able to keep up with the competition, which could eventually lead to lower profits or even bankruptcy.
Additionally, when capital expenditures are going down, it can also mean that there is less innovation happening in the economy. Without new investments in technology or research and development, businesses may struggle to stay competitive in the long term. This could slow down overall economic growth and potentially lead to a recession.
4. Purchasing power is in trouble as real earnings growth has been negative since January 2021 [4]
When real earnings growth is negative, it means that people's income is not keeping up with the rising cost of living. In other words, people are not making enough money to buy the same amount of goods and services as they used to. This is not good for the economy because it can lead to decreased consumer spending. When people have less money to spend, they are less likely to buy things, which can hurt businesses and their ability to grow and hire new employees.
Negative real earnings growth can also have a ripple effect on the stock market. Companies may see their profits decrease if consumers are not buying their products or services, which can lead to lower stock prices. Additionally, if people are struggling financially, they may not be able to invest in the stock market, which can further depress stock prices. Overall, negative real earnings growth can be a sign of an unhealthy economy that may need intervention from policymakers to stimulate growth and increase incomes for workers.
5. Consumer credit squeeze [5]
Credit card balances are on the rise while interest rates are increasing while people's personal financial situation is in one of the worst positions in a long time.
When credit card balances are on the rise, it means that people are spending more money on their credit cards than they can pay back. This is a problem because they will have to pay interest on that balance, which makes it harder to pay off in the future. Meanwhile, if interest rates are increasing, it means that the cost of borrowing money is going up. This can make it even harder for people to pay off their credit card balances, as the interest they owe will also increase.
When people's personal financial situation is in one of the worst positions in a long time, it means that they are struggling to make ends meet. This can be due to a variety of factors, such as job loss or an increase in expenses. If people are struggling to make ends meet, they may be more likely to rely on credit cards to cover their expenses, which can lead to an increase in credit card balances. This can create a cycle of debt that can be difficult to break free from. Overall, an increase in credit card balances and a worsening personal financial situation can be indicators of financial stress and economic hardship for individuals and the economy as a whole.
6. Inventories investments have been declining [6]
When inventories investments decline, it means that businesses are not stocking up on goods as much as they used to. This can indicate a few things about the economy. First, it may mean that demand for goods is slowing down, so businesses don't need to hold as much inventory to meet customer needs. Second, it may mean that businesses are uncertain about the future and don't want to take on the risk of holding large amounts of inventory that may not sell.
Either way, declining inventory investments can have ripple effects on the economy. For example, if businesses are not purchasing as many goods from suppliers, suppliers may see a decrease in sales and revenue. This, in turn, could lead to job losses and a decline in consumer spending. Additionally, if demand for goods does not pick up, it could lead to a slowdown in production and even a recession. Therefore, it's important for economists and policymakers to keep an eye on inventory investment trends and take action if necessary to support businesses and the overall economy.
7. Housing affordability at an all time low [7]
Housing affordability is a measure of how easy or difficult it is for people to afford to buy a home. When housing affordability is at an all-time low, it means that homes are becoming more and more expensive and it's becoming harder for people to afford to buy them. This can have a big impact on the economy as a whole.
For one, it can lead to a decline in the number of people who are able to buy homes, which can hurt the real estate industry. This, in turn, can lead to a slowdown in construction activity, which can have a ripple effect on other industries that rely on the construction sector. Additionally, when fewer people are buying homes, it can lead to a decline in consumer spending, as people are less likely to spend money on furnishings and other goods associated with homeownership.
Moreover, when housing affordability is low, it can also lead to social and economic inequality, as those who are unable to afford a home may be forced to rent or live in substandard housing, which can have negative impacts on their health and well-being. It can also exacerbate wealth inequality, as those who own homes may see their wealth increase, while those who don't may struggle to get by. All of these factors can have a significant impact on the economy, and it's important for policymakers to address them in order to ensure a healthy and stable housing market.
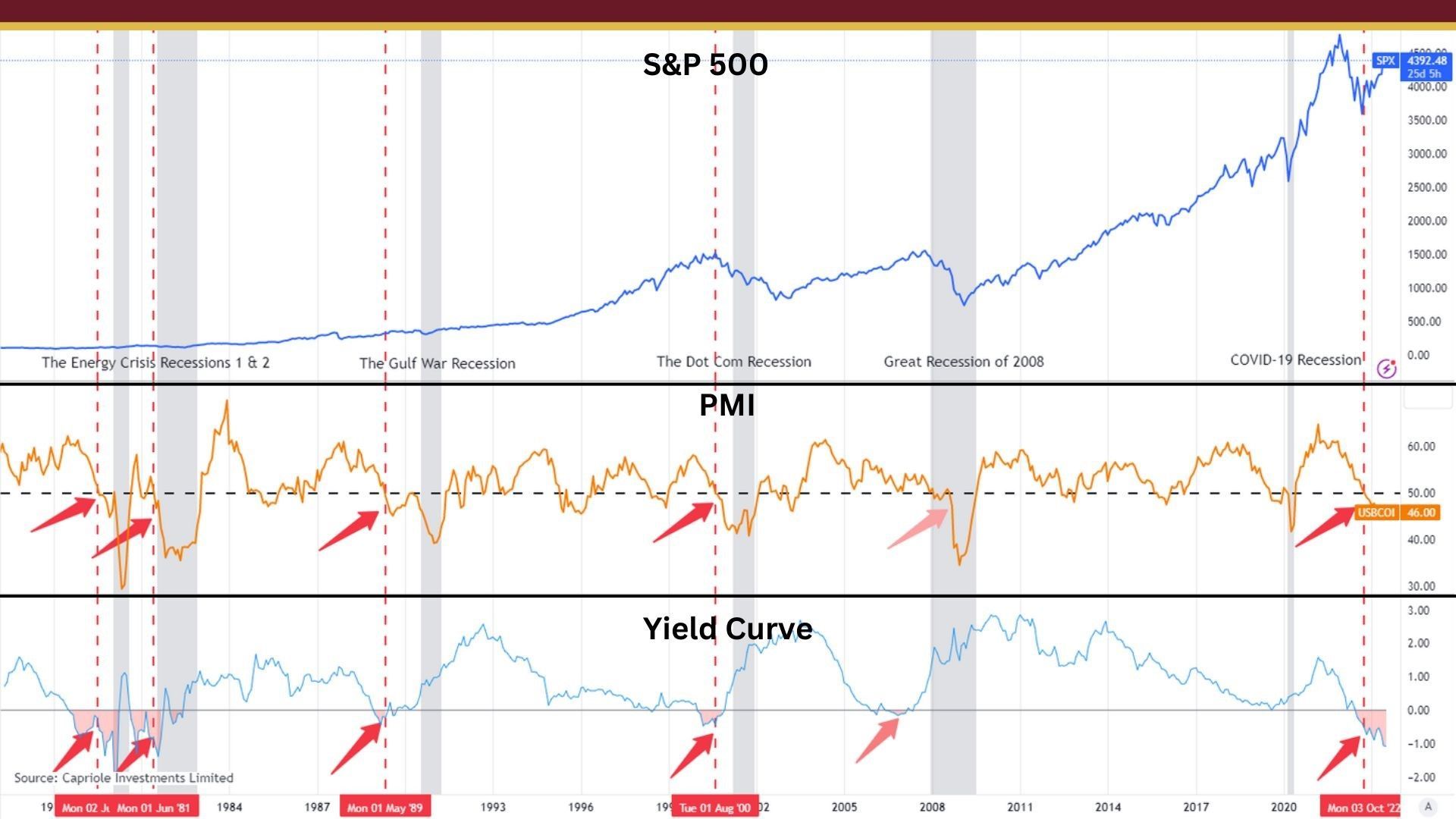
8. ISM services is reading as a contraction [8]
When the ISM services reading is in contraction, it means that the service sector of the economy is shrinking instead of growing. The Institute of Supply Management (ISM) releases monthly data on the performance of the service sector, which includes industries such as healthcare, finance, and retail. The data is based on a survey of purchasing managers in these industries and provides an important indicator of economic activity.
A contraction in the service sector is significant because it accounts for a large portion of the US economy. When businesses and individuals spend less on services, it can indicate a slowdown in consumer demand and overall economic growth. It can also mean that companies are cutting back on their hiring and investment plans, which can lead to higher unemployment and lower wages. Policymakers may use this information to adjust monetary and fiscal policies to stimulate economic growth and support businesses and households.
9. M2 - Money supply has been in the worst position since 1930s [9]
M2, also known as the money supply, is an important measure of the amount of money circulating in the economy. When M2 is in a bad position, it means that there is less money available to spend, invest, or lend. This can have a big impact on the economy, as people and businesses may struggle to access the funds they need to grow or make purchases.
The fact that M2 is in the worst position since 1929 is concerning, as this was the start of the Great Depression, a period of severe economic downturn. This suggests that the economy may be headed for another downturn or recession, as there may be less money available for businesses to invest, consumers to spend, and banks to lend. This can lead to a cycle of declining economic activity, job losses, and reduced consumer spending, which can further exacerbate the problem. It's important for policymakers and economists to monitor M2 and take steps to address any underlying issues that may be contributing to the decline in money supply.
10. ISM leads margin is lowering [10]
When we talk about the "ISM lead margin," we are referring to the gap between the prices that manufacturers pay for raw materials and the prices they can charge for finished goods. When this lead margin is decreasing, it means that manufacturers are paying more for raw materials than they can sell their finished products for. This is not a good sign for the economy, as it indicates that manufacturing is becoming less profitable.
When manufacturing becomes less profitable, it can lead to several negative effects on the economy. For example, manufacturers may cut back on production or lay off workers to save money. This can cause a ripple effect throughout the economy, as workers who have lost their jobs may have less money to spend on goods and services, leading to a decrease in demand for those goods and services. Additionally, if manufacturers are not making as much money, they may be less likely to invest in new equipment or technology, which can slow down innovation and economic growth over time. Therefore, a decreasing ISM lead margin is a warning sign for the economy that requires careful attention and analysis.
As these market conditions persist, it's going to be even harder to get money from banks, and people and businesses are going to have a hard time getting the money they need. This is because there are too many problems with things like prices going up and people not having jobs.
These problems are going to keep building up and things will only get worse. We can't be sure exactly when something really bad will happen, but we need to be ready for it because it could happen at any time.
Moving Forward
In tough times, people want to find something they can count on. In Quad 4, that "thing" is a group of three things: Gold, the US dollar, and Duration. Most things are getting cheaper because people aren't buying as much, but Gold has been going up in value.
We don't know how bad things will get because of decisions made by people in charge, but we do know that eventually they will have to do something to fix it. When that happens, they will probably print more money. Investors who know this are buying Gold now, so they can make money later when its value goes up even more. Gold is like a safe place to put your money when things are going bad.
Without a well thought out plan, your wealth is most likely to contract as the market and economy contracts.
Our goal at Abundance is to help you prosper regardless of the economy. Our Directional Portfolios aim to build a portfolio that will adjust with the business cycle. If you'd like to learn more, you can call or text at 678.884.8841 or email us at connect@findabundance.com.
Sources
- https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/DGDSRX1
- https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/AMTMNO
- https://www.yardeni.com/pub/ecoindsmbus.pdf
- https://budget.house.gov/press-release/fiscal-state-of-the-union-bidens-real-wage-decline/
- https://www.cnbc.com/2023/03/09/as-credit-card-debt-hits-new-high-households-near-a-breaking-point.html
- https://www.reuters.com/markets/us/us-business-inventories-fall-first-time-nearly-two-years-2023-03-15/
- https://www.entrepreneur.com/business-news/report-housing-affordability-is-at-an-all-time-low/447079
- https://www.spglobal.com/marketintelligence/en/mi/research-analysis/us-flash-pmi-signals-faster-economic-growth-in-march2023.html
- https://www.reuters.com/markets/funds/us-money-supply-falling-fastest-rate-since-1930s-2023-03-29/
- https://fred.stlouisfed.org/graph/?g=8cl
Schedule a Discovery Call


