By Tom Hermann (Chief Investment Officer)
•
May 12, 2023
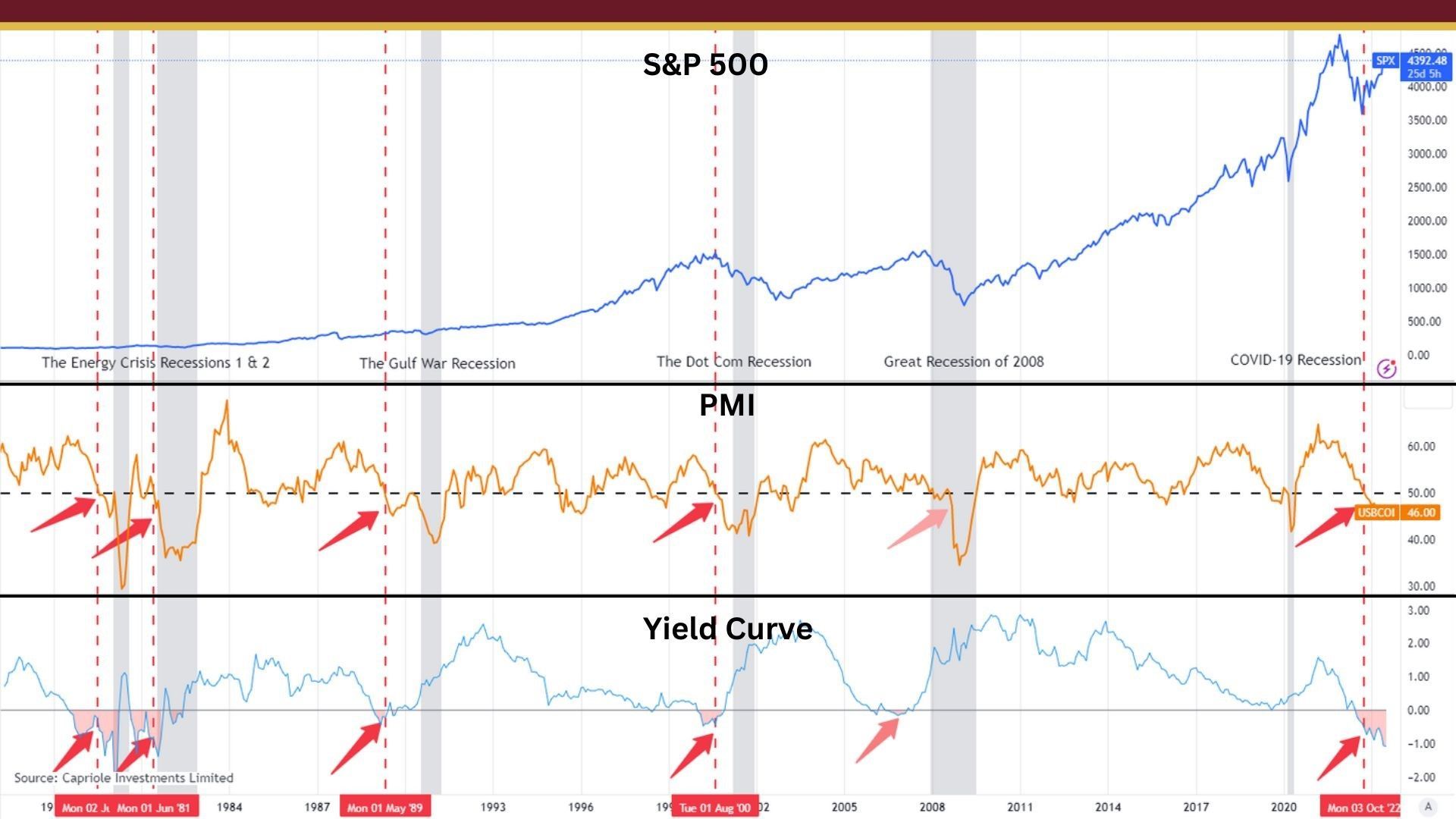
Are we heading towards a deflationary economy? The recent decline in manufacturing orders, ongoing banking crises, and a drop in small business optimism all point towards potential future unemployment rates on the rise. A deflationary economy is when prices for things we buy go down instead of up. This might sound like a good thing, but it can actually be a problem because it can cause people to stop spending money. In this week’s article, we will analyze a few of the recent economic indicators that support the existence of a deflationary economy. The Decline of German Manufacturing: What Does It Mean for the Rest of Europe? First, let's take a look at the manufacturing sector in Germany. The manufacturing sector continued to perform poorly in April 2023, with the worst performance since May of 2020. [1] The factory sector has been contracting for ten consecutive months. This has put continued downward pressure on new orders due to customer hesitancy and efforts to unwind buffer stocks. Average purchase prices fell the most since December of 2019, and expectations ticked up to a 14-month high. [2] When the average purchasing price of is going down, it means that manufacturers are paying less for the raw materials and other inputs needed to produce their products. Lower purchasing prices may seem like a good thing for manufacturers, as it means they can reduce their costs and potentially improve their profit margins. However, if prices continue to fall and the overall economy enters a deflationary period, it can have negative effects on the economy as a whole. In a deflationary environment, consumers and businesses delay spending and investment, expecting prices to continue to fall. This can lead to decreased demand, lower production, and ultimately, higher unemployment rates. The German economy is one to watch as it has historically been a one of the strongest in Europe. when Germany's economy is weak, it can have a negative impact on the rest of Europe. A slowdown in German manufacturing can lead to reduced demand for goods and services from other European countries, which can lead to lower economic growth and higher unemployment. Germany is also a major trading partner for many European countries, so any changes in Germany's trade policies or trade relations with other countries can have significant consequences for the rest of Europe. In addition, Germany plays a key role in the European Union (EU) and the Eurozone. As the largest economy in the Eurozone, Germany has a significant say in economic policy decisions that affect the entire region. Germany also provides significant financial support to other EU countries, particularly during times of economic crisis, so any changes in Germany's economic policies or priorities can have a ripple effect throughout the rest of Europe. It will be interesting to see how this develops as their economy could foreshadow what is next for the remainder of Europe. Lower Inflation: A Double-Edged Sword for the Global Economy The second indicator (or indicators) that we'll look at are inflation and employment data. The annual inflation rate for the US edged lower to 4.9% in April 2023, the lowest since April 2021, from 5% in March. [3] Food prices grew at a slower rate, and energy cost fell, namely gasoline and fuel oil. Shelter cost, which accounts for over 30% of the total CPI basket, slowed for the first time in two years. When you take out food and energy, the CPI rose 5.5% on the year and 0.4% on the month, in line with market forecasts. [4] Overall, the annual inflation rate in the US is expected to remain steady at 5% in April 2023, still much above the 2.1% average reported from 2000 to 2020. [5] Keep in mind the Federal Reserve has a dual mandate to promote price stability and maximum employment. The first role of the Fed is to keep inflation in check. They want to maintain stable prices and avoid both deflation (falling prices) and excessive inflation (rising prices). This is important because high inflation can erode the value of money, reduce purchasing power, and create economic uncertainty. The second role of the Fed is to promote maximum employment, which means achieving a level of unemployment that is consistent with full employment. This is important because high levels of unemployment can lead to reduced economic growth, lower consumer spending, and social problems. As you can see, there is still plenty of work to do when it comes to getting inflation back down to 2%, and the April employment information may support a Fed decision to keep raising interest rates. Total nonfarm payroll employment rose by 253,000 in April, and the unemployment rate changed little at 3.4%. [6] However, this month's report showed the change in total nonfarm payroll employment for February and March was revised down. With these revisions, employment in February and March combined is 149,000 lower than previously reported. [7] This is a sign that we're not adding jobs as fast as previously reported, which might mean that April's report could be revised down in the future. Also, the NFIB Small Business Optimism Index for April fell to it's lowest level since January of 2013, and reported that 49% of owners were expecting better business conditions over the next six months. [8] In other words, the majority of the small business owners surveyed believe that business conditions will get worse over the next six months. Considering the decline of demand that we're seeing in the economy, it would make sense that has business owners feel pressure financially that they'll have to resort to laying off workers. Banking crisis continues to cast a shadow on the economy Finally, a continued banking crisis points to the potential of a deflationary economy. This past week, PacWest stock plunged 23% after losing 9.5% of deposits. [9] We continue to see that people are concerned about the safety of their money being held with regional banks. This is concerning because regional banks are the biggest source of loans for small businesses. A small business is defined as a business with less than 500 employees. Using that designation, about half of the employed population in the US is employed by a small business. So let's connect the dots here. As regional banks continue to see their deposits decline, they will tighten their credit standards and be less willing to loan money. This will negatively impact small business loans and potentially place a heightened financial burden on the small businesses that are dependent on loans to keep operating. This will ultimately trickle down to the employees in the form of unemployment. Conclusion In conclusion, I think the economic indicators presented in this article support the beginning of a deflationary economy. It is important to note that a deflationary economy can have serious consequences for both individuals and businesses. Inflation can erode the value of savings and investments, but deflation can lead to a decrease in economic activity, which in turn can lead to job losses and reduced spending power. As consumers and business owners, it is crucial to pay attention to these economic indicators and adjust our strategies accordingly. For individuals, this may mean taking a more cautious approach to spending and investments, while for businesses, it may mean finding new ways to increase demand or streamline operations to reduce costs. Abundance is here to help you prosper regardless of what happens next in the economy. Our Directional Portfolios aim to build a portfolio that will adjust with the business cycle. If you'd like to learn more, you can call or text at 678.884.8841 or email us at connect@findabundance.com . The opinions expressed in this commentary are those of the author and may not necessarily reflect those held by Kestra Investment Services, LLC or Kestra Advisory Services, LLC. This is for general information only and is not intended to provide specific investment advice or recommendations for any individual. It is suggested that you consult your financial professional, attorney, or tax advisor with regard to your individual situation. Endnotes: HCOB Germany Manufacturing PMI, April 2023, https://www.markiteconomics.com/Public/Home/PressRelease/84c628d3c6e04e87a2660c3f940846a2 HCOB Germany Manufacturing PMI, April 2023, https://www.markiteconomics.com/Public/Home/PressRelease/84c628d3c6e04e87a2660c3f940846a2 Trading Economics, United States Inflation Rate, https://tradingeconomics.com/united-states/inflation-cpi Trading Economics, United States Inflation Rate, https://tradingeconomics.com/united-states/inflation-cpi Trading Economics, United States Inflation Rate Forecast, https://tradingeconomics.com/united-states/inflation-cpi/forecast U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, The Employment Situation - April 2023, https://www.bls.gov/news.release/pdf/empsit.pdf U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, The Employment Situation - April 2023, https://www.bls.gov/news.release/pdf/empsit.pdf National Federation of Independent Business, NFIB Small Business Optimism Index - April 2023, https://www.nfib.com/surveys/small-business-economic-trends/ Yahoo Finance, PacWest Stock Plummets 23% After Losing 9.5% of Deposits, https://finance.yahoo.com/news/pacwest-stock-plummets-23-losing-001937377.html