WHY RAISING INTEREST RATES IN A BANKING CRISIS COULD CRASH THE ECONOMY
Are you worried about your money in the bank? You're not alone. According to a recent poll by Gallup, nearly half of Americans are concerned about the safety of their money in banks. And with the continued failures of mid-size banks, those worries may not be unfounded. Despite this, the Federal Reserve has increased interest rates for the tenth consecutive time in an effort to curb inflation. But is inflation really the most pressing issue for the economy right now? In this week's update, we'll take a closer look at the potential risks of the Fed continuing to raise interest rates in the midst of a banking crisis, and explore the potential outcomes of such a move.
Another Rate Hike
Last week, the Federal Reserve increased interest rates by 0.25% for the tenth consecutive time. As previously discussed, this was done to curb inflation. However, as mid-sized banks continue to fail, it is becoming increasingly clear that inflation is not the most pressing issue for the economy. In fact, raising rates during a banking crisis can potentially cause significant damage to the economy.
Fed Chair Powell stated that the banking system is "sound and resilient." However, the general public seems to disagree. A recent Gallup poll conducted from April 3-25, 2023, before the most recent failure of First Republic Bank, showed that nearly half of Americans are concerned about the safety of their money in banks.
In our opinion, the Fed's margin of error is slim. Let's examine the potential outcomes if the Fed continues to raise rates during a banking crisis:
- Less money: By raising interest rates, the Fed would make it more expensive for banks to borrow money. This could lead to a reduction in liquidity in the banking system, making it harder for banks to meet their obligations and worsening the banking crisis.
- Increased defaults: Higher interest rates could also result in an increase in defaults on loans, as borrowers struggle to repay their debts. This could further weaken banks' financial position, as they may need to write off bad loans and incur additional losses.
- Slow economic growth: Raising interest rates during a banking crisis could also have a negative impact on the broader economy by slowing down economic growth. Higher interest rates can lead to a decrease in consumer spending and business investment, which can result in lower economic output and potentially lead to a recession.
- Negative market reaction: The announcement of a rate hike during a banking crisis could trigger a negative reaction in financial markets, as investors may perceive it as a sign that the Fed is not doing enough to support the economy. This could lead to a further decline in asset prices and an increase in market volatility.
We are already seeing signs of a negative market reaction, as eleven banks were down more than 17.5% last week, and PacWest Bank saw a decline of over 70%. These are not indicators of a banking system that is "sound and resilient."
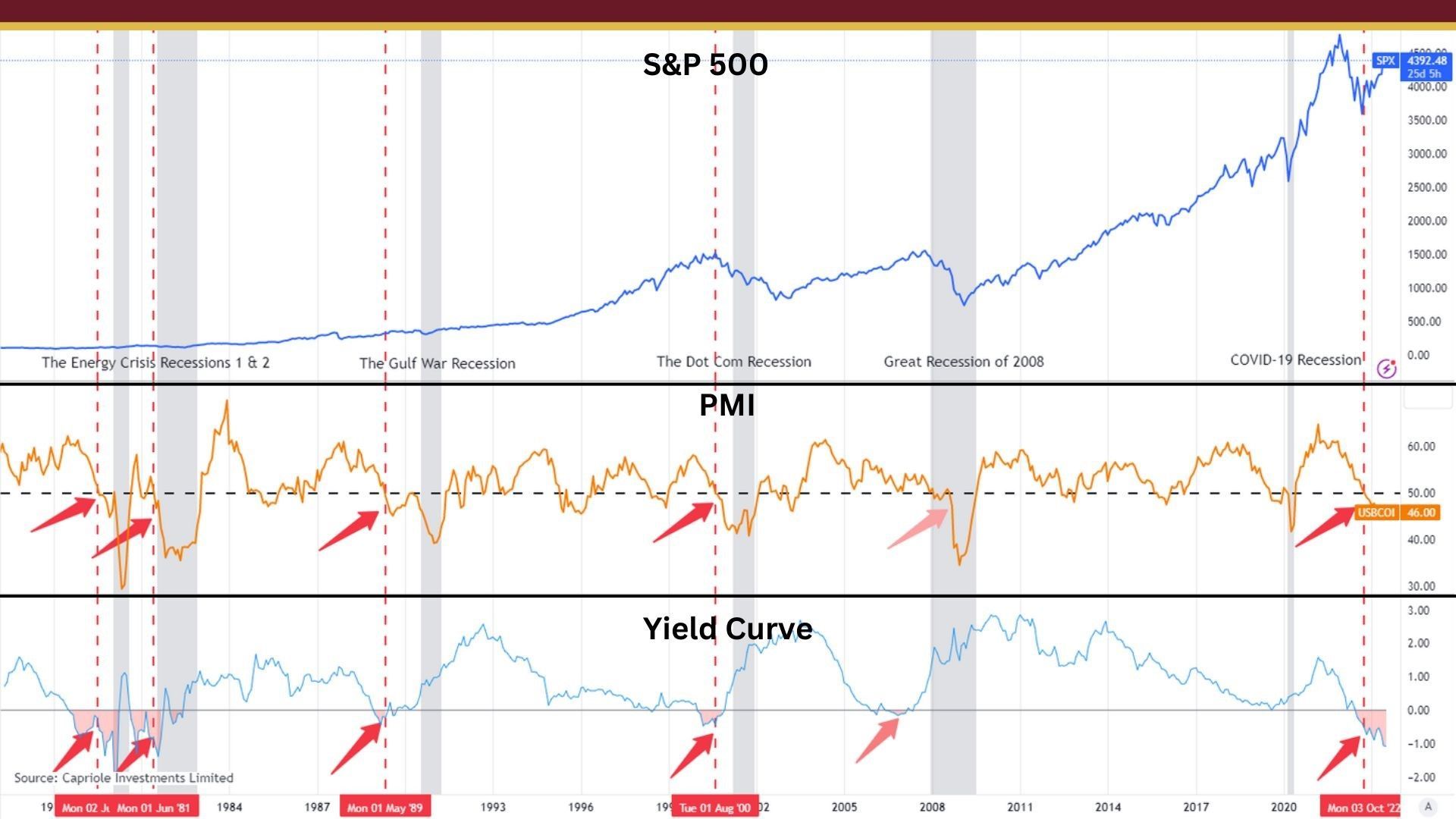
Crashing The Economy
At the beginning of the year, there was a lot of talk about a "soft landing." A soft landing occurs when the economy slows down or stabilizes without leading to a full-blown economic downturn or recession. This is characterized by a gradual decline in economic growth and inflation, and a smooth adjustment to new levels of economic activity. This can also be referred to as disinflation.
A soft landing is desirable because it allows the economy to adjust to new levels of growth without experiencing the negative effects of a recession, such as rising unemployment, falling incomes, and decreased economic activity. Essentially, disinflation is slowing down the rate of inflation to allow things to normalize. However, this is not the path we are currently on.
All signs point to an economic slowdown or deflation. Deflation is a sustained decrease in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over time. Deflation can be problematic for several reasons. Firstly, it can discourage spending by consumers and businesses because they know that prices are likely to be lower in the future, so they delay purchases. This can lead to a decrease in demand for goods and services, which can result in lower economic growth and increased unemployment.
Secondly, deflation can make it more difficult for borrowers to repay their loans. This can lead to defaults and bankruptcies, which can result in a decrease in the availability of credit, making it harder for businesses to invest and grow.
Thirdly, deflation can reduce profits for companies, which can lead to lower stock prices and a decrease in wealth for investors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the decision to raise interest rates during a banking crisis is a delicate balancing act for the Federal Reserve. While their primary goal is to curb inflation, they must also take into account the potential negative impacts on the banking system and the broader economy. The risks of raising rates during a banking crisis include reduced liquidity, increased defaults, slower economic growth, and a negative market reaction.
On the other hand, avoiding deflation and maintaining stable inflation is equally important for the health of the economy. The Federal Reserve must continue to carefully evaluate the situation and make decisions that prioritize both inflation and banking stability. With these factors in mind, we foresee turbulent times ahead. Abundance is here to help you prosper regardless of what happens next in the economy. Our Directional Portfolios aim to build a portfolio that will adjust with the business cycle. If you'd like to learn more, you can call or text at 678.884.8841 or email us at connect@findabundance.com.
The opinions expressed in this commentary are those of the author and may not necessarily reflect those held by Kestra Investment Services, LLC or Kestra Advisory Services, LLC. This is for general information only and is not intended to provide specific investment advice or recommendations for any individual. It is suggested that you consult your financial professional, attorney, or tax advisor with regard to your individual situation.
Schedule a Discovery Call


