COLLATERAL CRUNCH: HOW A SHORTAGE OF HIGH-QUALITY COLLATERAL IS AFFECTING FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS
Understanding the current state of the financial market can be a daunting task, especially when it comes to deciphering the importance of various rates and indicators. However, the Reverse Repurchase Program (RRP) and T-bill rates are two key factors that cannot be ignored. In short, the RRP rate is the interest rate paid by the Federal Reserve to financial institutions for borrowing money and using Treasury securities as collateral. On the other hand, the T-bill rate is the interest rate paid by the US government to investors for buying short-term securities to fund its operations.
Currently, there are concerns over the significant difference between the RRP and T-bill rates, which suggests that large institutions are prioritizing safety and risk management over higher returns. This situation could potentially lead to a further shortage of collateral and negative impacts on the overall economy. In this article, we'll explain what these rates are, why they matter, and what they might be signaling for the future market and economy.
What are RRP and T-bill rates?
The Reverse Repurchase Program (RRP) is a tool used by the Federal Reserve to manage the money supply and short-term interest rates. In simple terms, the Fed borrows money from financial institutions and offers Treasury securities as collateral. The interest rate paid by the Fed to the institutions for this borrowing is called the RRP rate.
On the other hand, Treasury bills are short-term securities issued by the US government to fund its operations. These securities are considered low-risk, which makes them an attractive investment option for financial institutions. The interest rate paid by the government to the investors for buying T-bills is called the T-bill rate.
Why do RRP and T-bill rates matter?
RRP and T-bill rates are important indicators of the supply and demand for high-quality collateral in the market. Financial institutions, such as banks, need high-quality collateral to secure their borrowing and lending activities. This collateral is often required by regulators to manage the risks that financial institutions take on in their day to day operations. High-quality collateral, such as U.S. Treasury bills, is considered safe and low risk, providing lenders with assurance that they will be able to recover their funds in case of default.
When the demand for such collateral exceeds the supply, it can cause the rates to diverge significantly. This can indicate a lack of confidence in the economy and could be a sign of an impending financial crisis.
Moreover, these rates can affect the overall monetary policy of the Federal Reserve. If the RRP rate is significantly higher than the T-bill rate, it may cause financial institutions to prefer lending money to the Fed instead of investing in T-bills. This could lead to a shortage of T-bills in the market, which may negatively impact the overall economy.
Current concerns
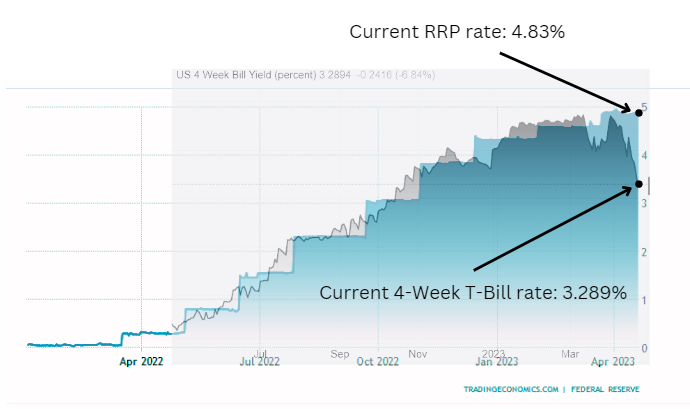
Currently, there are concerns over the significant difference between the RRP and T-bill rates. As of April 20, 2023, the RRP rate was 4.83%, while the 4-week T-bill rate was 3.289%. This creates concern because it suggests that there is an underlying shift where large institutions are looking for safe investments. Let's take a look at how this works.
First, you need to understand how the relationship between the price and interest rates work for fixed income investments. In essence, the rate of return on a fixed income investment goes down as the price goes up. For example, bonds are a common fixed income investment and generally trade at $1,000 per bond. Therefore, a 4% yield on a $1,000 bond will generate $40 of interest.
Now, if those 4% bonds are in high demand then you may have to pay $1,100 for that bond instead of the $1,000. That bond will still pay the $40 of interest (…hence the name fixed income. The interest payment is fixed). However, since you paid $1,100 for the $40 of interest your return of investment is now 3.63%.
Intuitively, it should make sense that your rate of return will be less if you pay more for an investment that will produce the same amount of cash flow of $40.
If you look at the chart above, you will see that 4-week T-Bill rate has been on decline since the beginning of April. This would indicate that investors are buying more of these bonds driving the price up which in turn drives the rate of return down.
So why is this a concern?
The main concern is that this significant difference may indicate a shortage of high-quality collateral in the financial markets. These institutions need collateral (like T-Bills) to meet their regulatory requirements and manage their risks. This is telling because it’s a sign that financial institutions are willing to make a lower return on their money to prioritize safety and risk management.
We see an example of how T-Bills were used as a risk management tool in Silicon Valley Bank. They were forced to sell their T-Bills as the customers of the bank were starting to take their money out. Since the bank didn't have all the deposits on hand they had to create cash by selling their T-Bills.
Another concern is that this situation could lead to a flight to safety by major financial institutions. If they perceive that there is a lack of confidence in the market, they may prefer to park their money in the safest possible option, such as US Treasury securities. This could cause a further shortage of collateral, which may negatively impact the overall economy.
These concerns should not be a surprise as we see an uptick, from commercial real estate to the US government, of people struggling to meet their loan obligations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the significant difference between the RRP and T-bill rates is currently a cause for concern in the financial market. While it is not necessarily a sign of an impending financial crisis, it does indicate a shortage of high-quality collateral in the market, and leads us to believe that there are significant concerns about the markets and the economy. Abundance is here to help you prosper regardless of what happens next in the economy. Our Directional Portfolios aim to build a portfolio that will adjust with the business cycle. If you'd like to learn more, you can call or text at 678.884.8841 or email us at connect@findabundance.com.
[Chart sources: RRP rate and 4 week T-Bill Rate]
Schedule a Discovery Call


